Entity Multi-Currency Processing in Ascent Finance Platform
Entity/Multi-Currency Processing in Ascent Finance Platform
In order to support our customers who prefer to work in multiple currencies and provide the ability to track transactions by business entity, the Ascent Finance Platform (AFP) supports multi-currency and provides continuity of processing for entities as defined by the Ascent Main package within AFP defined objects (Cash Entry, Applied Cash Receipt, Refund, Journal Entries, etc..).
Some examples of the functionality that is provided by AFP in a multi-currency organization:
- AFP Journals report is the currency of the transaction being journaled.
- Account currency totals (total outstanding balance, total unapplied payments, etc…) are automatically maintained in the account currency when the individual transaction lines (which may be in different currencies) are being aggregated for totals.
- Currencies constrain what previous transactions can be used in an AFP transaction. For example, if an applied cash receipt is being credited to a Sales Invoice, only cash entries in the currency of the sales invoice can be used for the applied cash receipt.
- Org Exchange Rates (the conversion factor from the transaction or journal currency to the org currency) are maintained on AFP objects such as cash entry, applied cash receipt, refunds, etc… (This is in addition to the conversion rates maintained by Ascent Main, on its own objects).
Entity functionality provided by AFP to support entity processing in Ascent Main (when turned on by configuration):
- AFP journals can report their currency amounts in the currency assigned to the entity of the journaled transaction. This occurs when the AFP custom setting “Use entity currency for journals” is turned on and entities are turned on in Ascent Main.
- AFP objects (payments, applied payments, refunds, etc) will inherit the entity of the transaction it is being recorded against. For example, if a payment is being recorded against a Sales Order, the payment will receive its entity assignment automatically from the entity assigned to the sales order.
Accessing these Features
Multi-currency functionality is automatically enabled when multi-currency is detected as being turned on within the org. In addition, the design of the AFP multi-currency support, assumes the following additional configuration:
- Usage of Advanced multi-currency. (Parenthetical multi-currency can be turned on, but is strongly not recommended, because of the potential of creating significant confusion in how Salesforce performs currency conversion versus the currency conversion being performed by Ascent Main and AFP). However, there is a custom setting within Ascent ERP that simulates the Salesforce custom setting. If desired, this can be enabled:

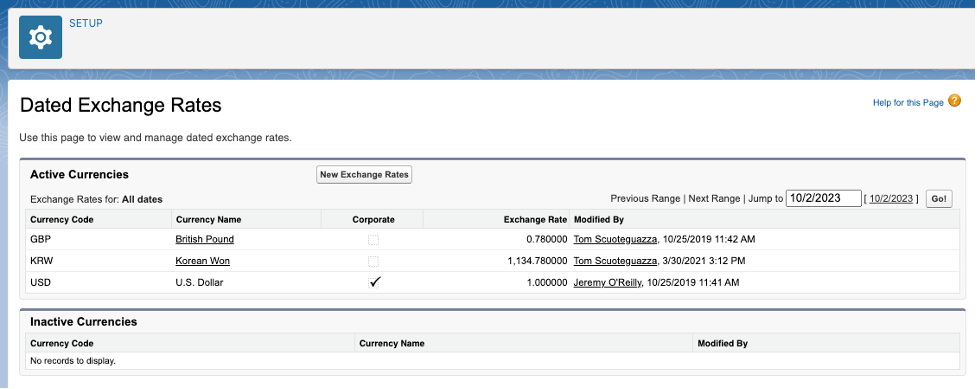
AFP also assumes setup of dated exchange rates for each currency in use. This is necessary, because some journals have the potential to do currency conversion that reflect the conversion rate in effect on the date of the original transaction, not the current system date:
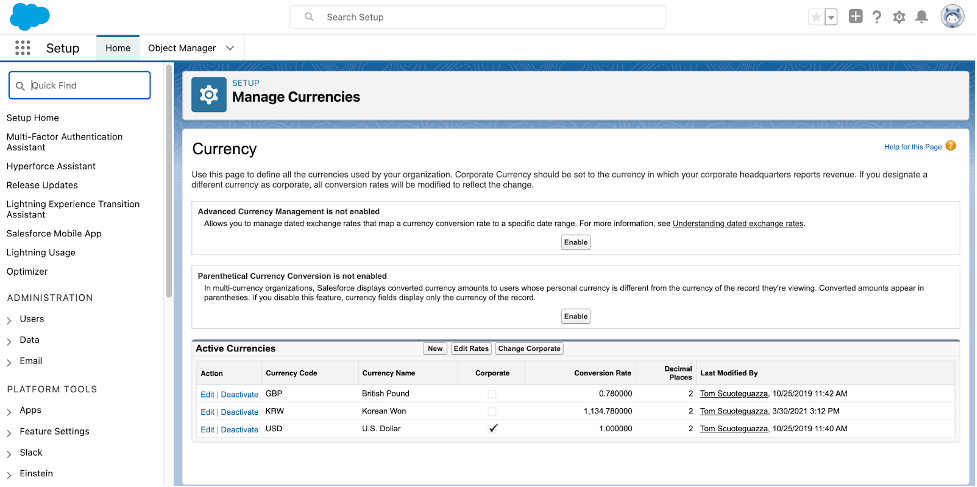
- If journals are to be reported in entity currency, change the setting, “Use Entity Currency for Journals” in the AFP Custom Settings screen:
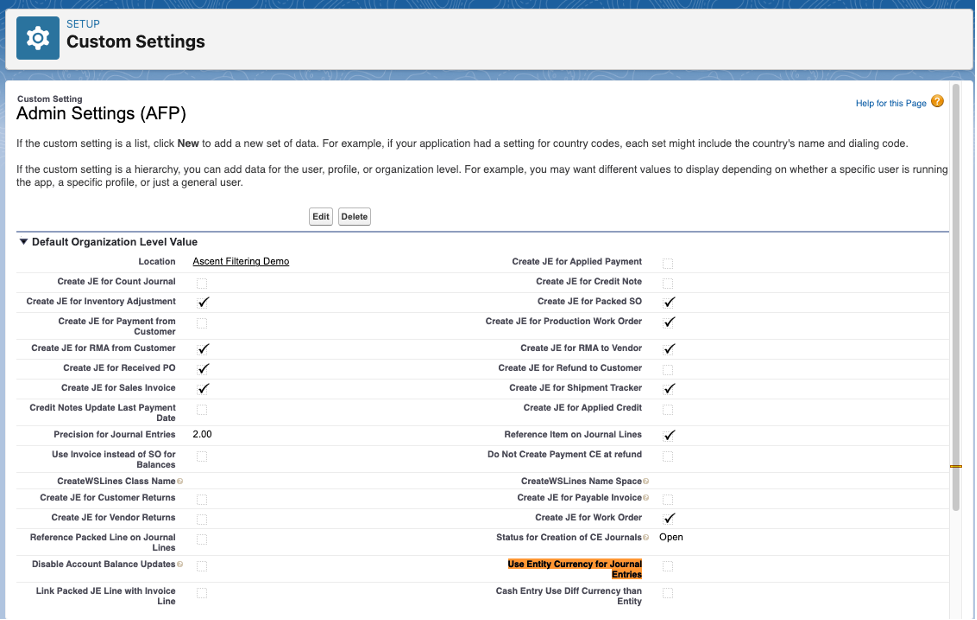
- If currency conversion is required to entity currency on AFP journals, the proper currency code needs to be assigned on each entity record held in the Entity object:
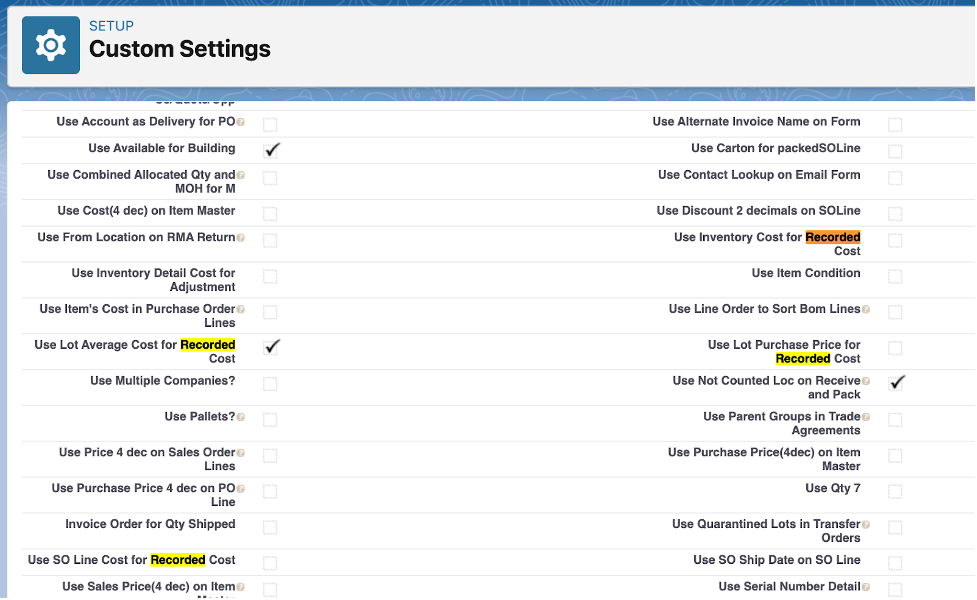
In addition, the inventory cost value on the journal entry line can come from multiple areas, depending on which custom setting is selected:
Demonstrating Multi-currency and Multi-Entity in Action
In this example, a sales order will be packed, to demonstrate that the packed sales order journal is created in the currency of the sales order:
- First, the org currency, is defined in US Dollars (USD):
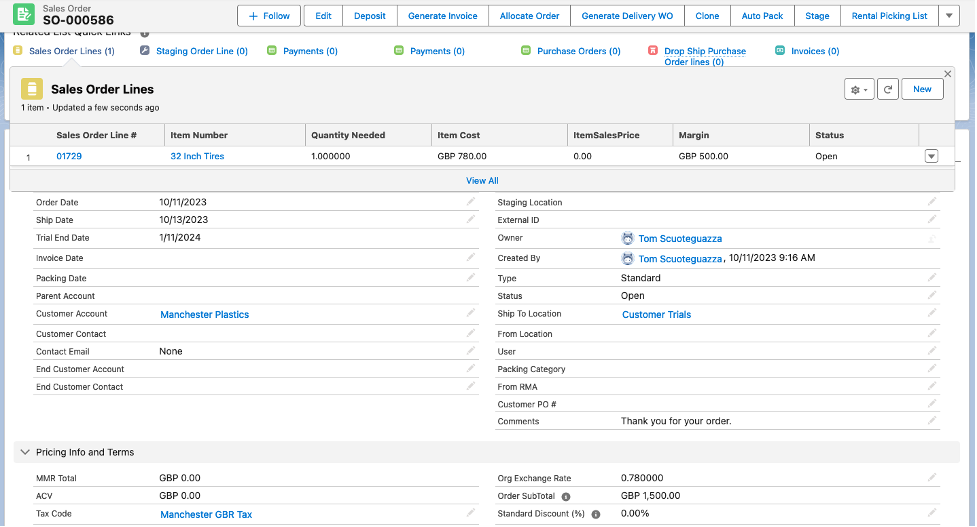
- Create a Sales Order in GBP (GBP):
- Packing the sales order, results the following journal entry:
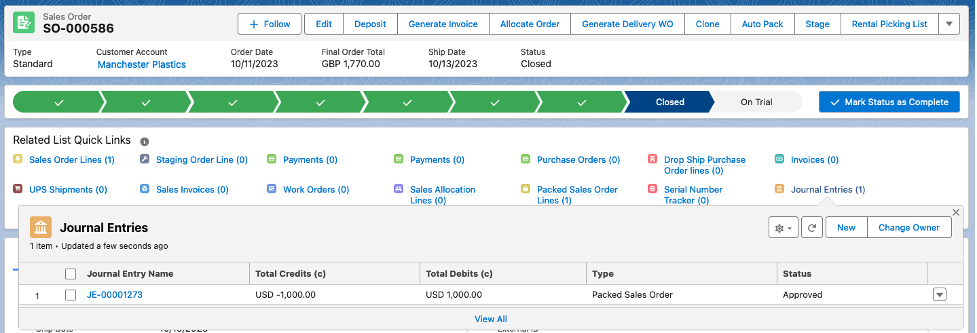
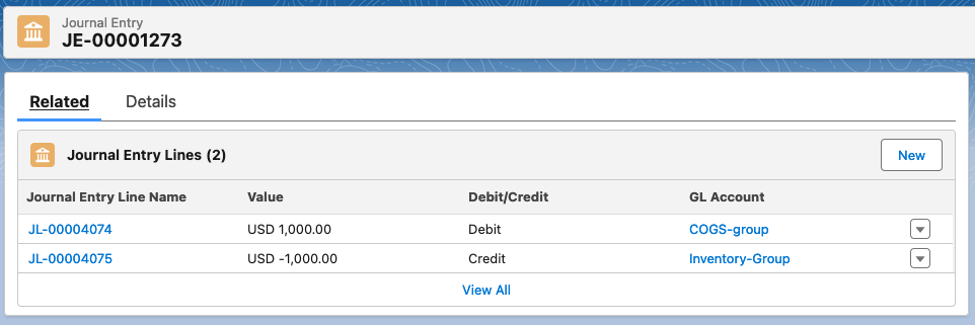
The recorded journal cost of 1000 USD, reflects the lot average cost item recorded cost of USD 1000 multiplied by a packed quantity of 1. The currency on the Sales Order is GBP, but we are logged into the Entity 1: US entity, which uses the currency of USD.
While not presented on the previous sales order screen, notice how Entity (Entity 1: US) was automatically assigned to the packed sales order journal. This journal entry can now be used to summarize the packed out recorded costs of sales lines by entity.
In creating the supporting inventory for this sales order pack example, a purchase order was created/received and a production work order was created/built, These transactions resulted in the following journal entries:
Received PO Line, Lot Cost Information, and Received Purchase Order Journal:
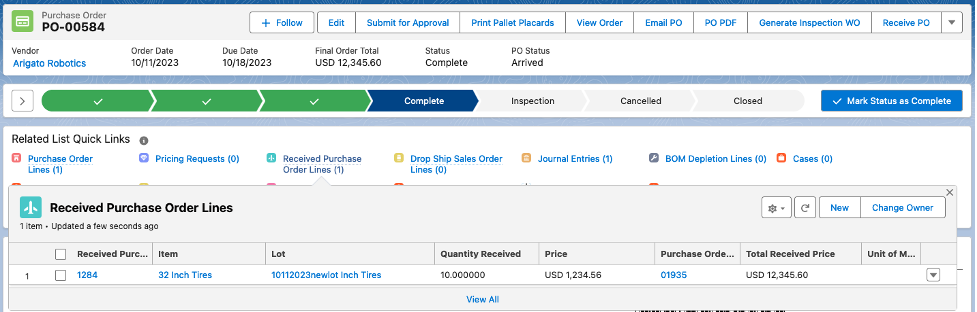
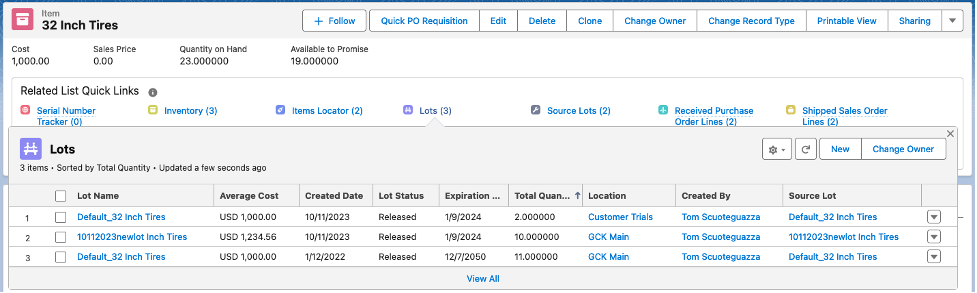
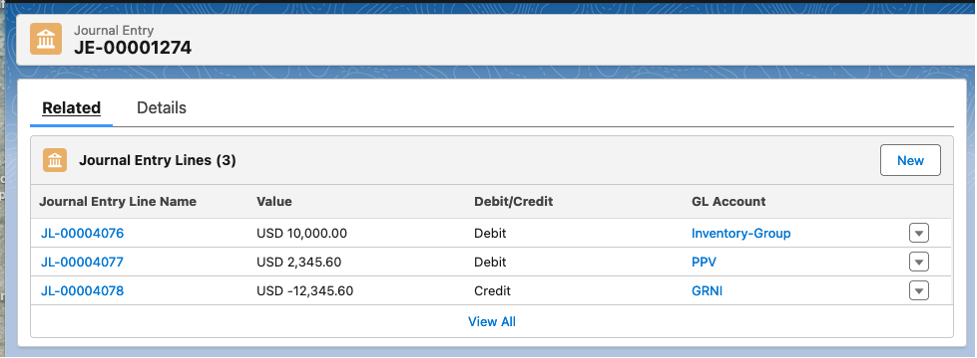
Notice the Journal costs (PO purchase price) were automatically reported in USD. Also, the entity’s currency was automatically assigned to the journal.
Production Work Order Journal:
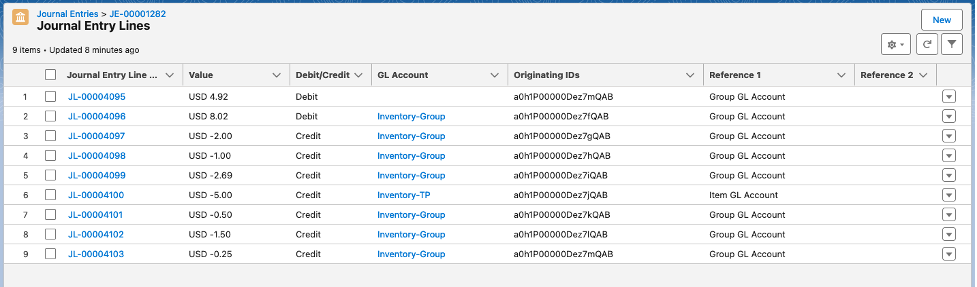
Finally, observe the PWO material variance calculation is also reported in USD.
Demonstrating Journal Conversion to Entity Currency
In this example, we are going to create a sales order in USD, but assign it to an entity whose currency is in GBP. The AFP setting for using entity currency for journals is in effect. The result of creating and packing the sales order:
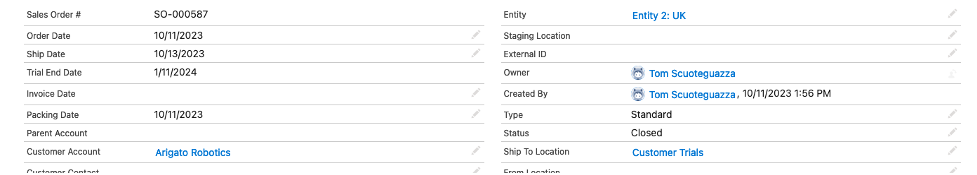
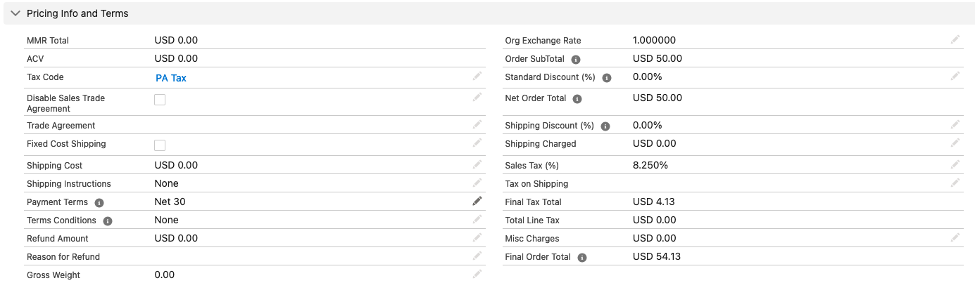
The sales order is in US Dollars, but an entity is assigned to the sales order with GBP currency.
The resulting packed sales order journal:
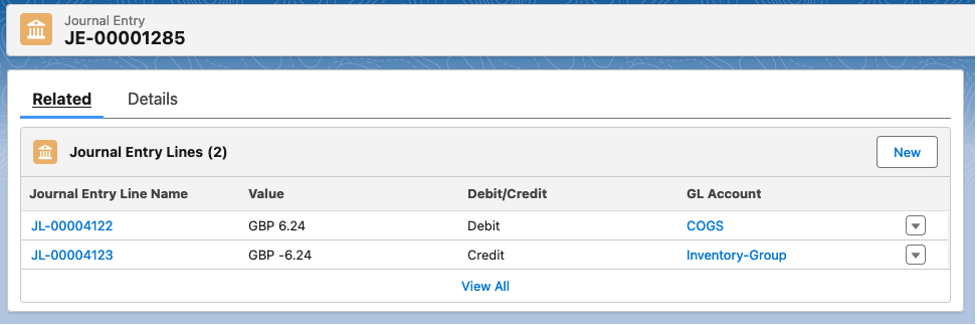
The resulting packed sales order journal is in GBP. It was packed from a location assigned to a European entity.
Finally, if one were to drill down on one of the journal entry lines, to display the detail on the journal entry line:
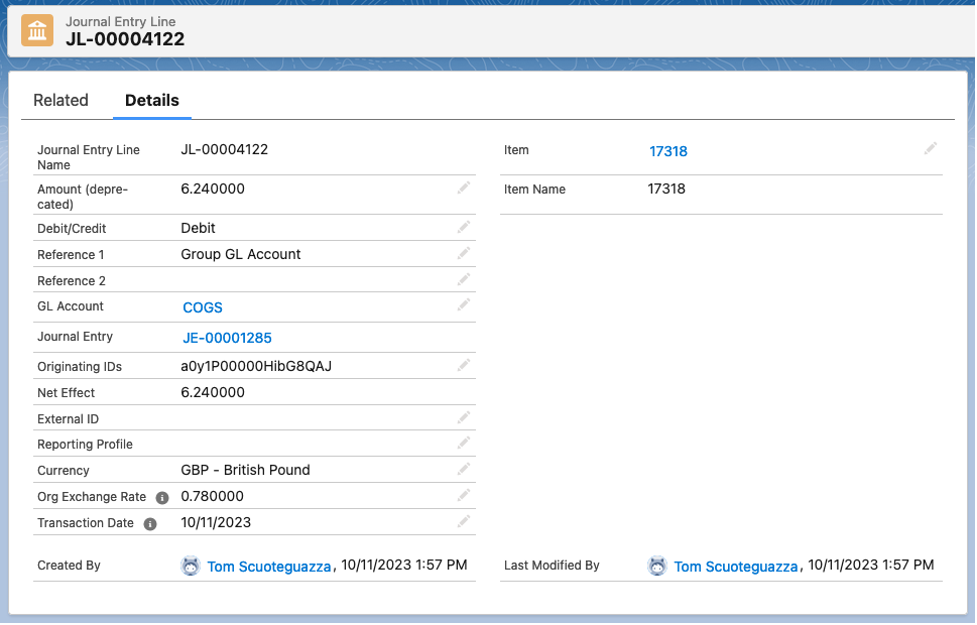
There are now two fields, Org Exchange Rate and Transaction Date.
Org Exchange Rate is the conversion rate to convert the currency amounts from USD back to the user entity currency (GBP). This is done by multiplying the currency amount by the Org Exchange Rate. e.g. USD 8.00 * .78 (EUR/USD) = GBP 6.24.
The Transaction Date is the date used to lookup the dated exchange rate from USD to GBP. Transaction date, in this particular example, is the date the sales order line was packed.
